Nature of light? Provide a comprehensive description with each image.
Light is a fascinating phenomenon that has captivated scientists and philosophers for centuries. It’s the very essence of our perception of the world, allowing us to see, experience color, and even feel warmth. But what exactly is light? It’s a fundamental force of nature, a form of electromagnetic radiation that travels in waves. These waves oscillate in electric and magnetic fields, carrying energy and information across vast distances.
Let’s explore the nature of light through different perspectives:
1. Light as a Wave:
Imagine a pebble dropped into a still pond. Ripples spread outward, demonstrating the wave-like nature of light. Light waves, however, are far more complex, oscillating in electric and magnetic fields. These oscillations are what determine the color of light.
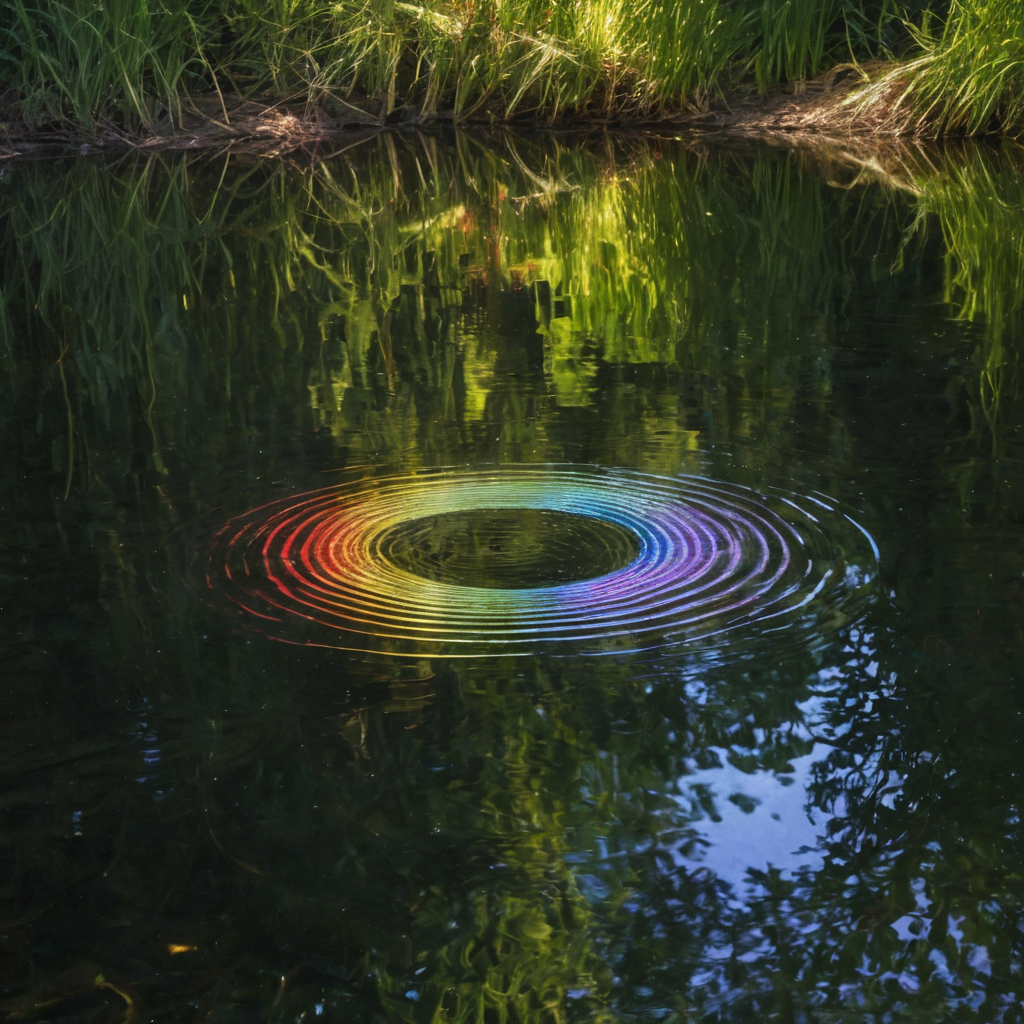

2. Light as a Particle:
While light behaves as a wave, it also exhibits particle-like properties. These particles are called photons, tiny packets of energy that carry light’s momentum.

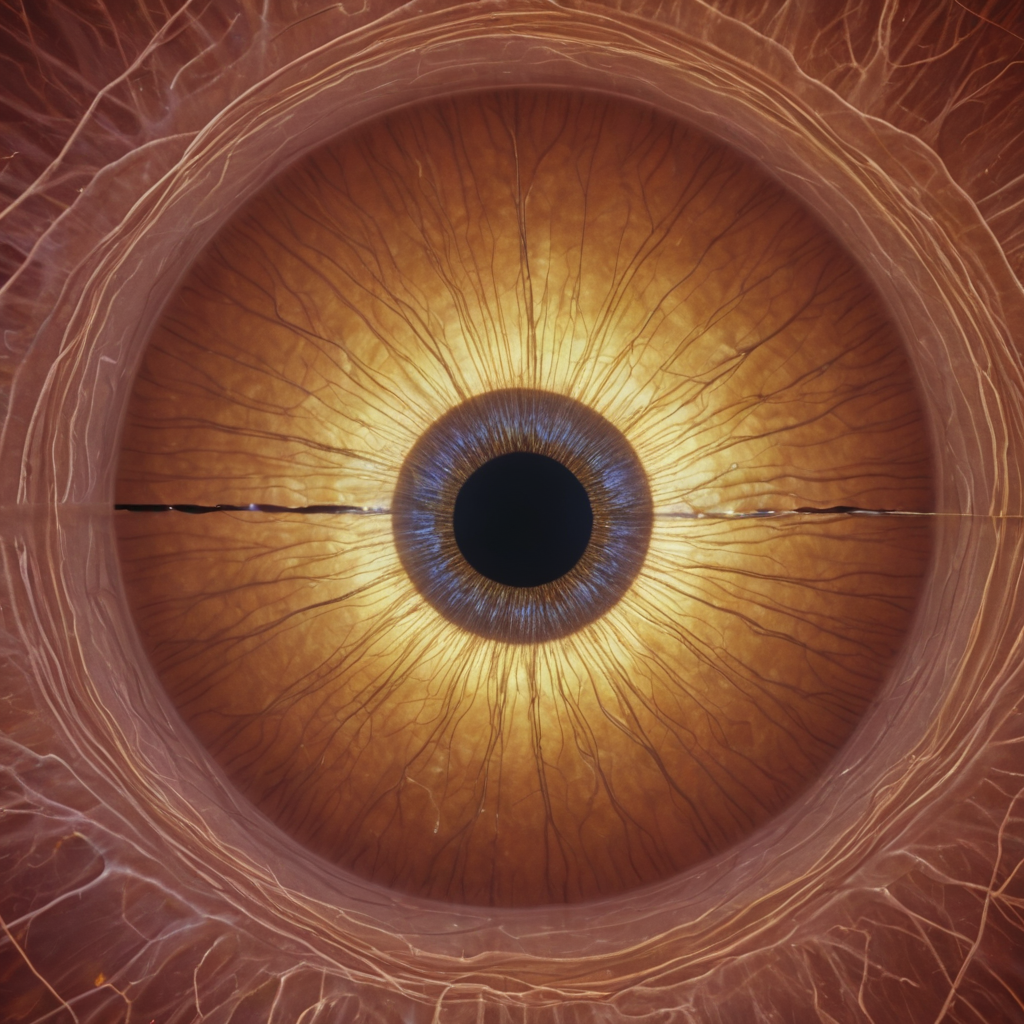
3. Light and our Perception:
Our eyes are exquisitely sensitive to light. When light enters the eye, it stimulates cells called photoreceptor cells, triggering a chain reaction that ultimately sends signals to our brain. These signals are interpreted as images, colors, and shapes, allowing us to perceive the world around us.
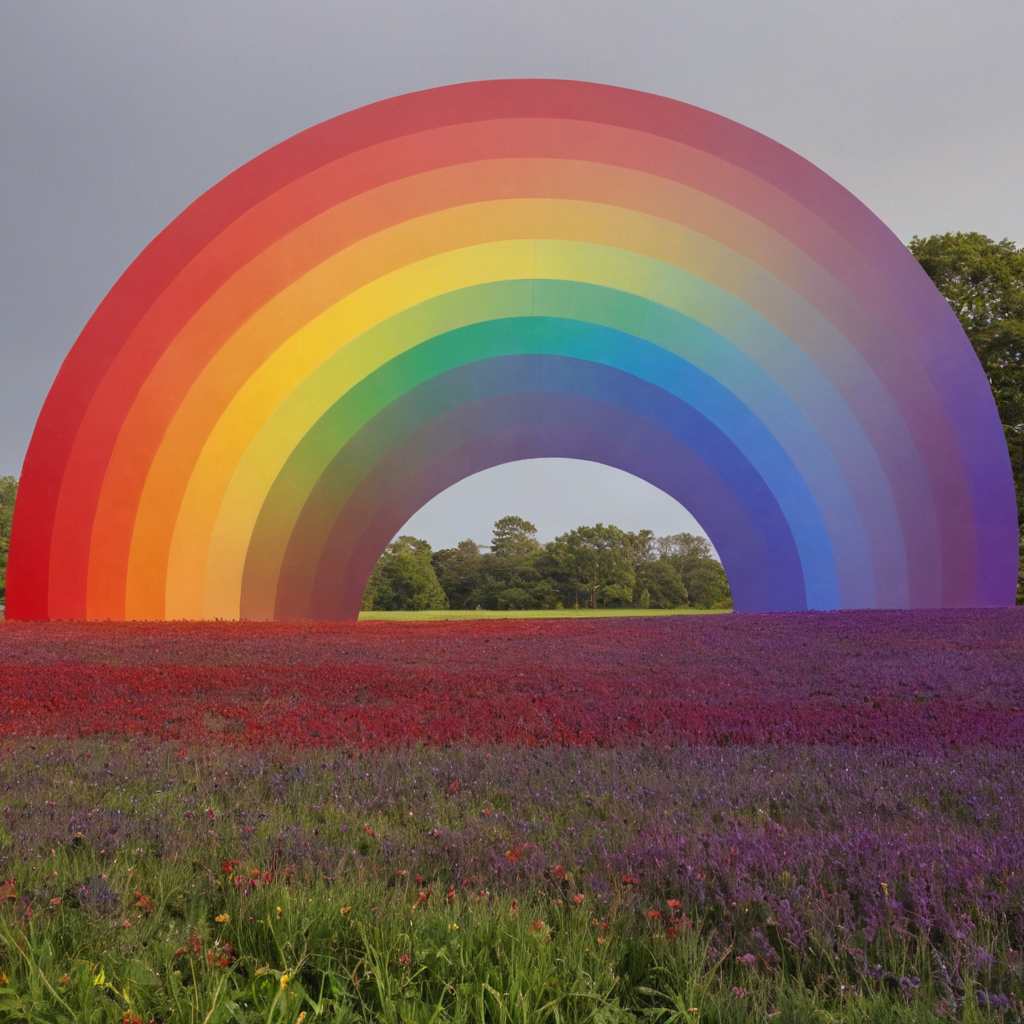
Explain the relationship between the frequency and color of light.
The frequency of light determines its color. The higher the frequency, the bluer the color. The lower the frequency, the redder the color. Think of it like a rainbow – red has the lowest frequency and violet the highest.

What is the relationship between the energy and color of light?
The energy of light is directly proportional to its frequency. This means that higher frequency light has more energy. Since the color of light is determined by its frequency, higher energy light will appear bluer, while lower energy light will appear redder.

Can you give me an example of how energy and color are related in everyday life?
Think about a stovetop. When you turn on a burner, it starts to glow red. As you increase the heat, it gets hotter and the color changes to orange, then yellow, and finally a very bright white. This is because as the energy of the burner increases, the frequency of the light it emits also increases. This change in frequency causes the color of the light to change.





